I started the year using Gemini Pro to take our integration patterns and covert them into “playing card” style pattern library so that we can print and play! The content is mine, I used AI to generate the images with still a few issues with image text – oh well, maybe something to refine later in 2026 or next year.
In this post we follow from simple real time read/writes to bulk/batch cases. Remember the question I asked at the end of our read post? How do you use simple query patterns to read a collection? (Hint: pagination). In this post, we will look at only some of the bulk read patterns especially focussing on consumer initated. I am guessing you are already familiar with producer initated such as simple file transfer with is AR-0 and omitted for brevity
So, bulk read is rarely “just export a file”. It is a job lifecycle with state, pagination, retries, and resumability. These patterns formalise that lifecycle, keen to see how many you have implemented – any?
Included patterns
- AR-1 — Asynchronous Bulk Read – Consumer Adapter Request + Polling
- AR-2 — Asynchronous Bulk Read – Consumer Adapter Request + Provider Events
- AR-3 — Asynchronous Bulk Read – Consumer System Request + Adapter (Events/Shared Location)
- AR-4 — Asynchronous Bulk Read – Consumer System Request + Polling (No Events)
AR-1: Asynchronous Bulk Read – Consumer Adapter Request + Polling
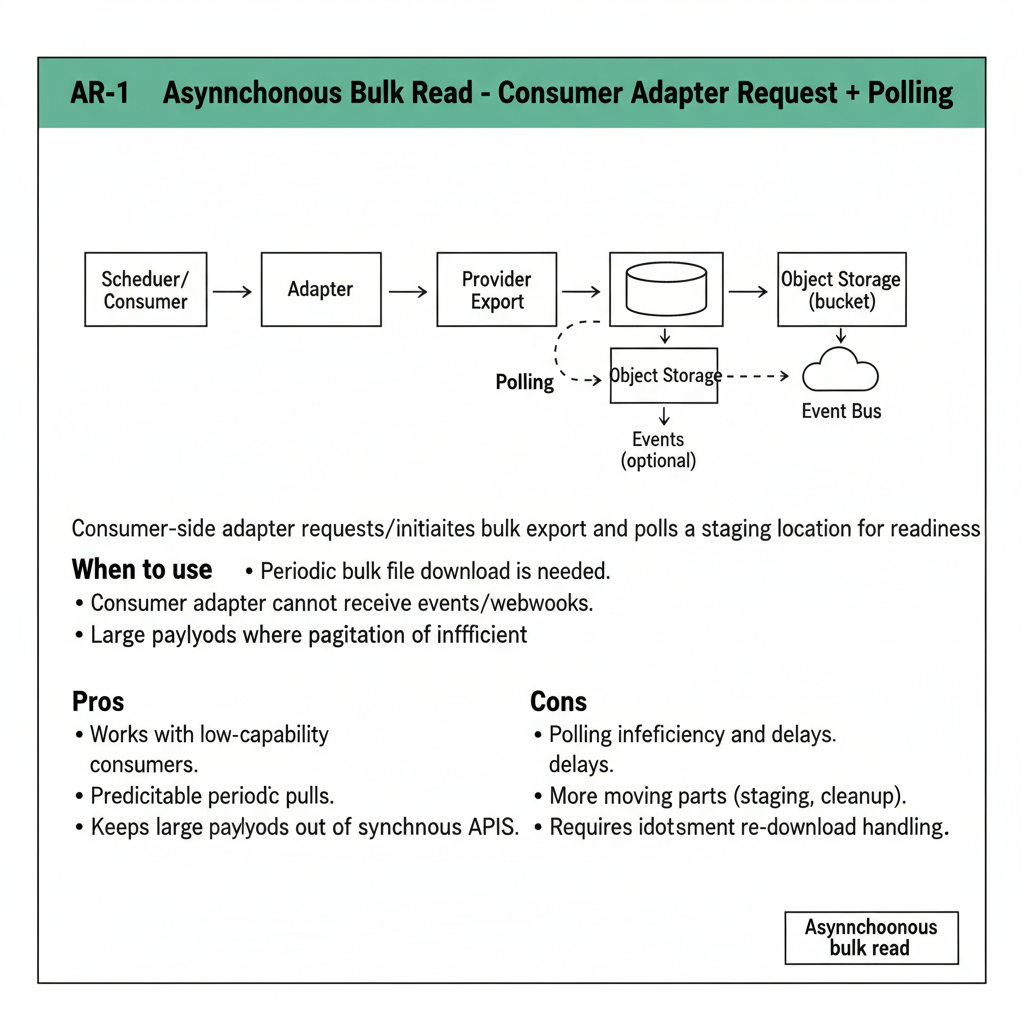
Consumer-side adapter requests/initiates bulk export and polls a staging location for readiness.
When to use
- Periodic bulk file download is needed.
- Consumer adapter cannot receive events/webhooks.
- Large payloads where pagination is inefficient.
Pros
- Works with low-capability consumers.
- Predictable periodic pulls.
- Keeps large payloads out of synchronous APIs.
Cons
- Polling inefficiency and delays.
- More moving parts (staging, cleanup).
- Requires idempotent re-download handling.
PlantUML
@startuml
title Asynchronous Bulk Read - Consumer Adapter Request + Polling
actor "Scheduler" as Scheduler
participant "Consumer Adapter" as Consumer_Adapter
participant "Provider Export API" as Provider_Export_API
participant "Provider Staging (S3/SFTP)" as Provider_Staging__S3_SFTP_
Scheduler -> Consumer_Adapter: Start periodic export job
Consumer_Adapter -> Provider_Export_API: Request bulk export
Provider_Export_API -> Provider_Staging__S3_SFTP_: Write export file
Consumer_Adapter -> Provider_Staging__S3_SFTP_: Poll for file readiness
Provider_Staging__S3_SFTP_ -> Consumer_Adapter: File available
@endumlAR-2: Asynchronous Bulk Read – Consumer Adapter Request + Provider Events
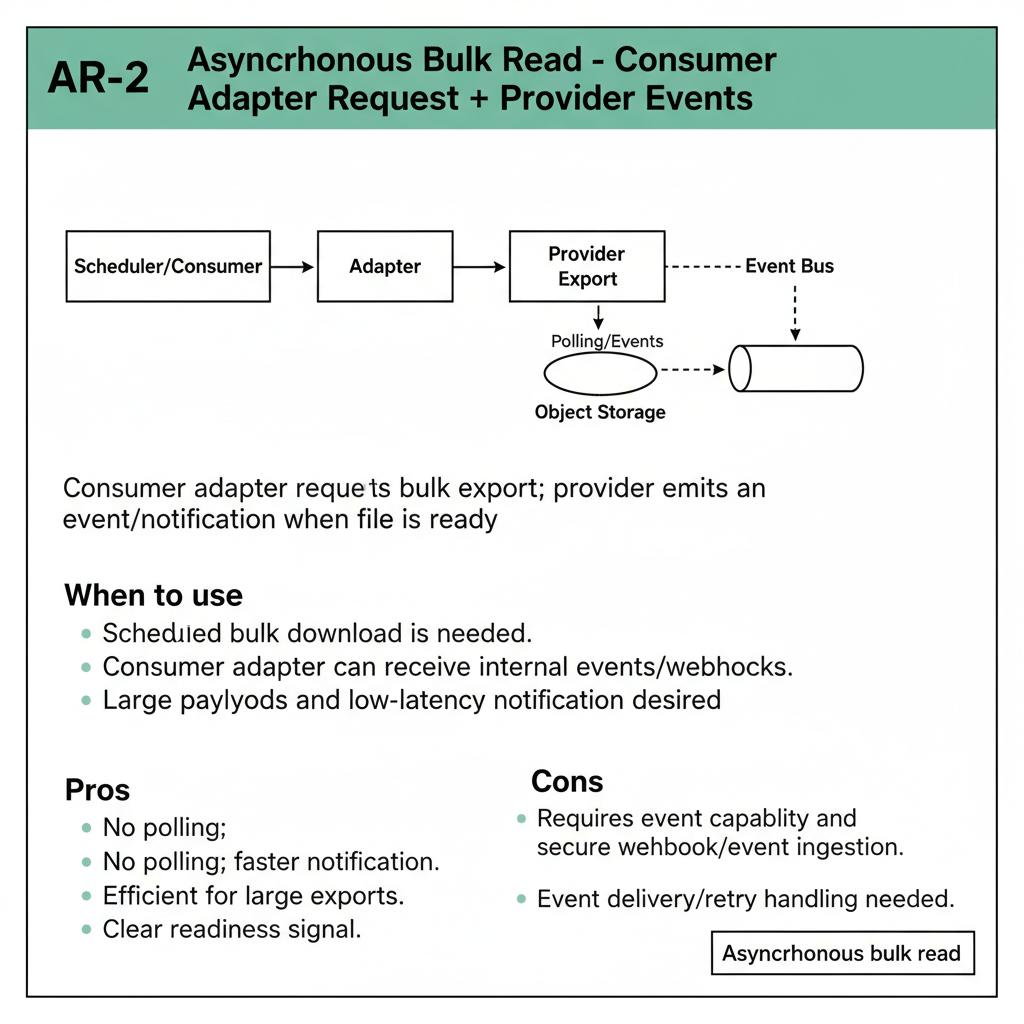
Consumer adapter requests bulk export; provider emits an event/notification when file is ready.
When to use
- Scheduled bulk download is needed.
- Consumer adapter can receive internal events/webhooks.
- Large payloads and low-latency notification desired.
Pros
- No polling; faster notification.
- Efficient for large exports.
- Clear readiness signal.
Cons
- Requires event capability and secure webhook/event ingestion.
- Event delivery/retry handling needed.
PlantUML
@startuml
title Asynchronous Bulk Read - Consumer Adapter Request + Provider Events
actor "Scheduler" as Scheduler
participant "Consumer Adapter" as Consumer_Adapter
participant "Provider Export API" as Provider_Export_API
participant "Event Bus" as Event_Bus
participant "Provider Staging (S3/SFTP)" as Provider_Staging__S3_SFTP_
Scheduler -> Consumer_Adapter: Start periodic export job
Consumer_Adapter -> Provider_Export_API: Request bulk export
Provider_Export_API -> Provider_Staging__S3_SFTP_: Write export file
Provider_Export_API -> Event_Bus: Publish BulkReady(exportId, location)
Event_Bus -> Consumer_Adapter: Deliver BulkReady
Consumer_Adapter -> Provider_Staging__S3_SFTP_: Download file
@endumlAR-3: Asynchronous Bulk Read – Consumer System Request + Adapter (Events/Shared Location)
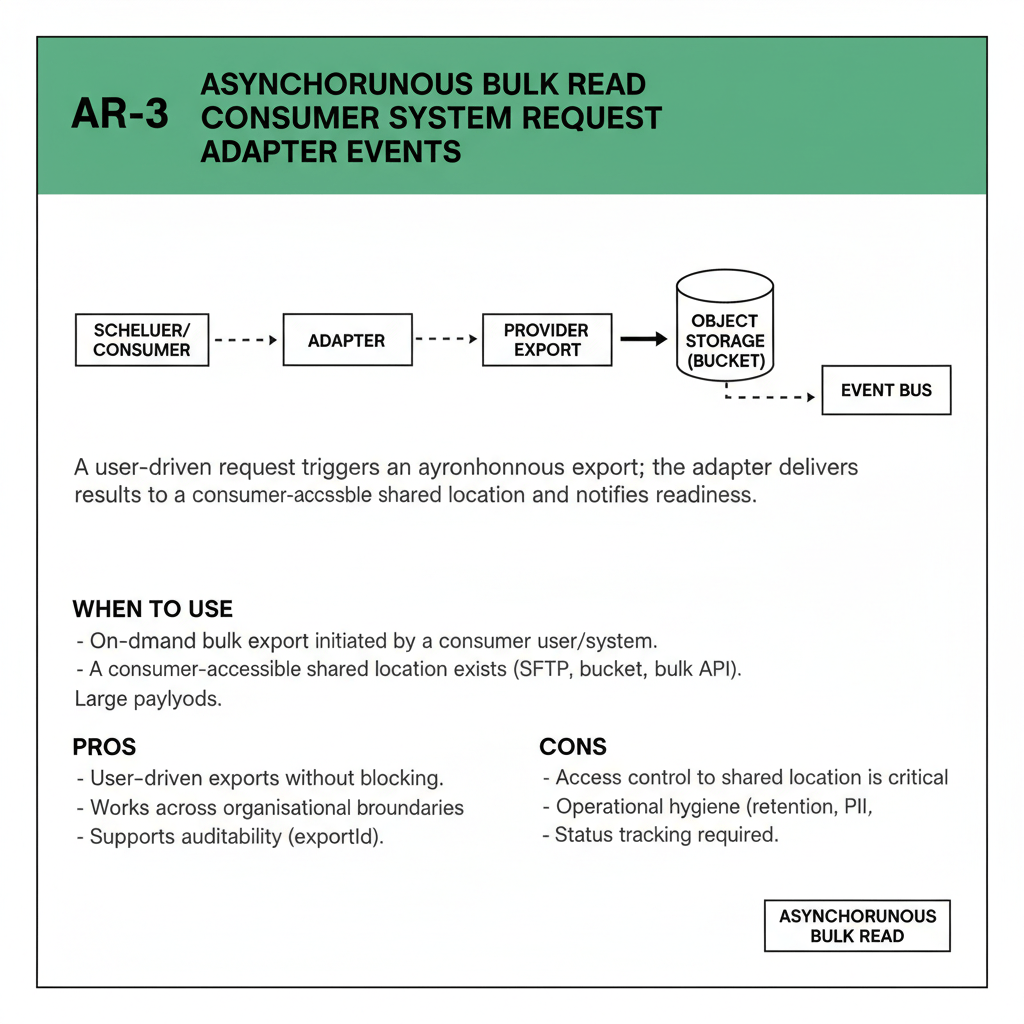
A user-driven request triggers an asynchronous export; the adapter delivers results to a consumer-accessible shared location and notifies readiness.
When to use
- On-demand bulk export initiated by a consumer user/system.
- A consumer-accessible shared location exists (SFTP, bucket, bulk API).
- Large payloads.
Pros
- User-driven exports without blocking.
- Works across organisational boundaries.
- Supports auditability (exportId).
Cons
- Access control to shared location is critical.
- Operational hygiene (retention, PII).
- Status tracking required.
PlantUML
@startuml
title Asynchronous Bulk Read - Consumer System Request + Adapter (Events/Shared Location)
actor "Consumer System" as Consumer_System
participant "Consumer Adapter" as Consumer_Adapter
participant "Provider Export API" as Provider_Export_API
participant "Provider Staging" as Provider_Staging
participant "Consumer Shared Location" as Consumer_Shared_Location
participant "Event Bus" as Event_Bus
Consumer_System -> Consumer_Adapter: Request export (criteria)
Consumer_Adapter -> Provider_Export_API: Request bulk export
Provider_Export_API -> Provider_Staging: Generate export file
Provider_Export_API -> Event_Bus: Publish BulkReady(exportId, location)
Event_Bus -> Consumer_Adapter: Deliver BulkReady
Consumer_Adapter -> Consumer_Shared_Location: Push file to shared location
Consumer_Adapter -> Consumer_System: Notify export ready (exportId, link)
@endumlAR-4: Asynchronous Bulk Read – Consumer System Request + Polling (No Events)
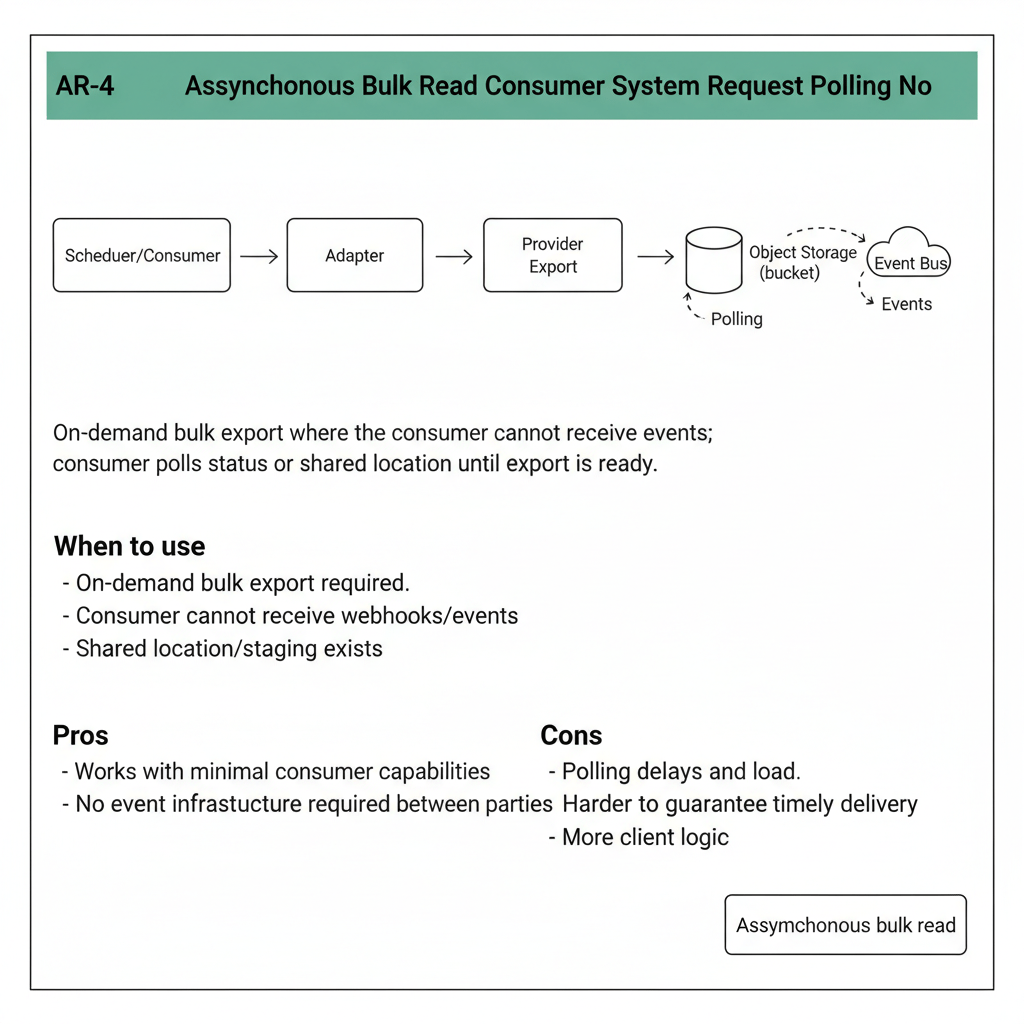
On-demand bulk export where the consumer cannot receive events; consumer polls status or shared location until export is ready.
When to use
- On-demand bulk export required.
- Consumer cannot receive webhooks/events.
- Shared location/staging exists.
Pros
- Works with minimal consumer capabilities.
- No event infrastructure required between parties.
Cons
- Polling delays and load.
- Harder to guarantee timely delivery.
- More client logic.
PlantUML
@startuml
title Asynchronous Bulk Read - Consumer System Request + Polling (No Events)
actor "Consumer System" as Consumer_System
participant "Consumer Adapter" as Consumer_Adapter
participant "Provider Export API" as Provider_Export_API
participant "Provider Staging" as Provider_Staging
participant "Consumer Shared Location" as Consumer_Shared_Location
Consumer_System -> Consumer_Adapter: Request export (criteria)
Consumer_Adapter -> Provider_Export_API: Request bulk export
Provider_Export_API -> Provider_Staging: Generate export file
Consumer_System -> Consumer_Adapter: Poll export status
Consumer_Adapter -> Provider_Staging: Check readiness
Provider_Staging -> Consumer_Adapter: Ready + location
Consumer_Adapter -> Consumer_Shared_Location: Push file
Consumer_Adapter -> Consumer_System: Return ready + link
@endumlSummary
We looked at some of the bulk read patterns which are consumer initated, these can of course be as simple as producer initated and simple file transfer with is AR-0 and omitted for brevity
Before any implementation, we must start with the following
- Define the contract first (schema, idempotency key, ordering expectations)
- Define bulk handling failure, who is getting this data and how are we defining success
- Instrument job state and failure modes (metrics + searchable logs) especially if not using MFT tools